The healthcare sector in Australia is at the forefront of technological transformation, with smart integration and electrification—including the critical shift towards degasification—emerging as key drivers of change.
These advancements are reshaping infrastructure, influencing lifecycle planning, and redefining capital investment strategies. This article delves deeper into the tangible impacts and value propositions, supported by real-world examples from Victoria (VIC), New South Wales (NSW), and Queensland (QLD).
The Push Towards Smart Integration and Electrification
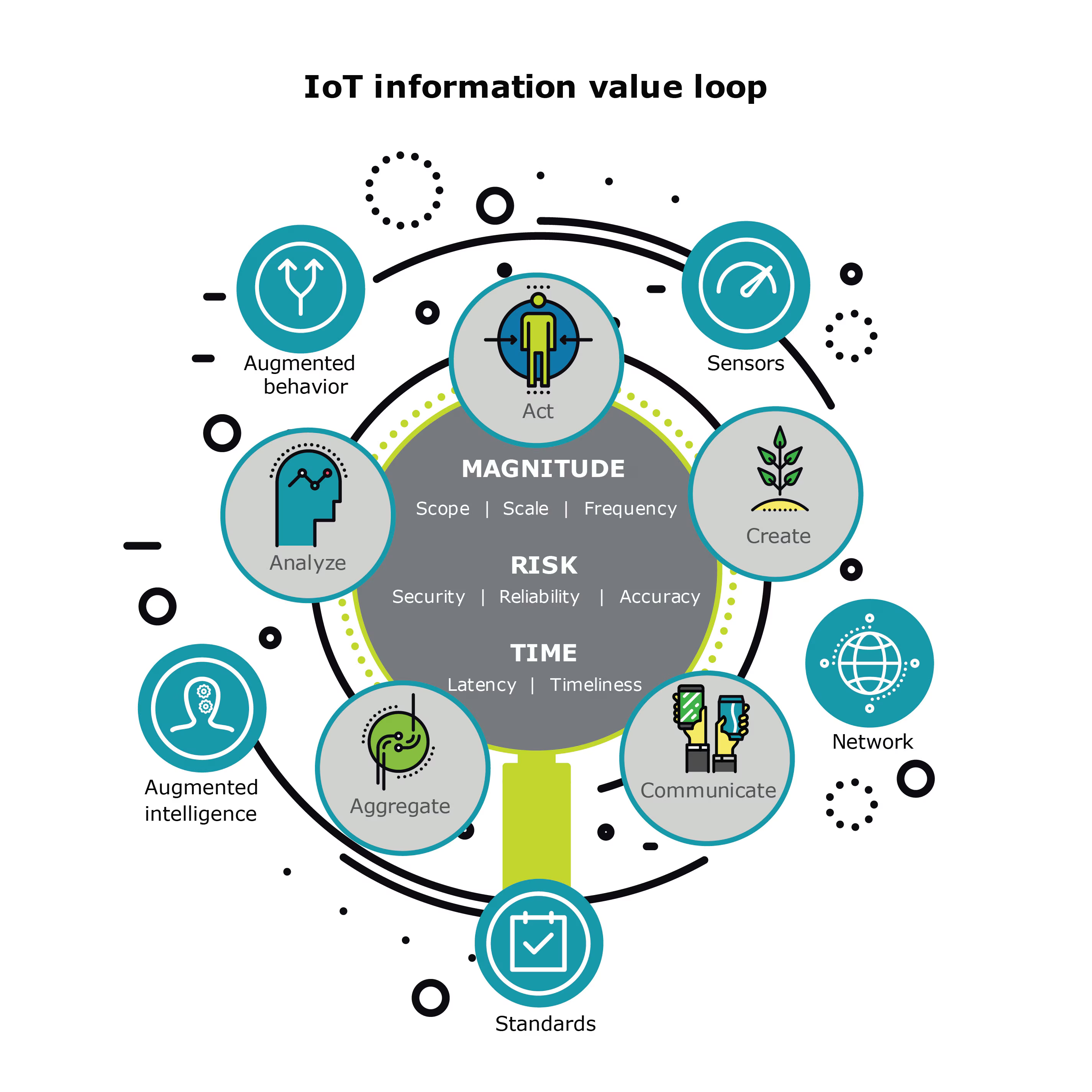
Smart integration involves combining advanced technologies such as IoT, AI, and robotics to create cohesive, responsive systems within healthcare facilities. Electrification, including degasification, entails replacing fossil fuel-based systems with electrified or renewable energy solutions for heating, cooling, and powering medical equipment, alongside comprehensive infrastructure upgrades and building capital works.
Source: ABB Industry Case NZ
Key Drivers:
Improved Patient Care: Real-time monitoring through IoT-enabled devices reduces response times and enhances diagnostics. A study by PwC found that smart healthcare systems can improve patient outcomes by up to 25% through timely interventions.
Operational Efficiency: Advanced Building Management Systems (BMS) integrated with predictive analytics reduce energy costs by an average of 30%, according to the Australian Energy Market Operator (AEMO).
Environmental Sustainability: A report by CSIRO highlights that electrification and renewable energy adoption can cut healthcare facility emissions by over 40% when coupled with energy-efficient retrofits.
Implementation Strategies
Implementing smart integration and electrification requires careful planning, collaboration, and the use of proven strategies to ensure successful outcomes. These strategies can guide healthcare facilities in achieving their goals.
Comprehensive Infrastructure Assessment: Conduct energy audits to identify potential areas for degasification and electrification. For example, a 2023 report by Engineers Australia recommended prioritizing HVAC and lighting systems for electrification in healthcare facilities, achieving ROI within five years.
Stakeholder Collaboration: Align objectives across healthcare providers, contractors, and government bodies to streamline project delivery. An AIA study found that collaborative planning reduced project delays by 18% in recent electrification projects.
Phased Investment Plans: Implement upgrades in stages to balance budget constraints and minimize disruptions. Hospitals in NSW adopting phased electrification saved 15% on upfront costs compared to full-scale implementations.
Resilience Planning: Invest in infrastructure capable of handling variable energy loads, incorporating battery storage to maintain uninterrupted operations during peak demands.
Contract Models and Their Role
Contract models play a critical role in facilitating the adoption of electrification and smart integration in healthcare facilities. Selecting the right model ensures optimal project execution and risk management.
Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs): Used extensively in projects like the Sunshine Coast University Hospital, PPPs offer a balanced risk-sharing model, fostering innovation and ensuring financial sustainability.
Energy-as-a-Service (EaaS): Emerging as a game-changer, EaaS models enable facilities to adopt electrification technologies without capital outlay, with guaranteed energy savings of up to 20%, according to ARENA.
Design-Build-Operate (DBO): This model ensures a seamless transition from construction to operations, delivering up to 25% operational efficiency improvements in complex healthcare environments.
Asset Lifecycle and Sustainability Operations
Effective asset lifecycle management is essential for ensuring the long-term success of electrification and smart integration projects. Sustainability operations further enhance the value and impact of these initiatives.
Maximizing asset performance while ensuring sustainability requires:
Lifecycle Cost Analysis (LCCA): Evaluating the total cost of ownership, including energy savings and maintenance. Research by the Green Building Council of Australia shows electrified systems reduce lifecycle costs by 30% compared to gas-based systems.
Retrofitting Strategies: Replace obsolete gas systems with modern electrified solutions. For instance, Sunshine Coast University Hospital’s retrofitting program resulted in a 20% increase in HVAC efficiency.
Predictive Maintenance: Utilize IoT sensors to monitor equipment health, reducing unplanned outages by 25%, as observed in Westmead Health Precinct.
Renewable Integration: Combine solar, wind, and battery storage to ensure reliability and sustainability, achieving energy cost reductions of up to 40% in hospitals like Gold Coast University Hospital.
Value Propositions
The transition to electrification and smart integration offers significant value propositions for healthcare facilities. These benefits extend beyond cost savings to include enhanced operational resilience and environmental compliance.
Enhanced Asset Value: Electrification and degasification boost asset longevity, reduce maintenance costs by up to 25%, and improve building valuation.
Capital Investment Optimization: Phased implementation aligns with budget cycles, ensuring financial feasibility while delivering long-term operational savings.
Environmental Compliance: Adherence to Green Star and NABERS standards enhances reputation and reduces penalties associated with carbon emissions.
Operational Excellence: Integrated systems lower downtime, improve patient care delivery, and generate a measurable ROI within 7-10 years.
Industry Insights and Statistics
The Australian Energy Regulator (AER) highlights that healthcare facilities implementing electrified systems save between $500,000 and $1 million annually on energy costs.
A 2024 report by Infrastructure Australia estimates that renewable energy adoption in healthcare buildings can reduce lifecycle costs by 30%-35%.
Research by Deloitte indicates that IoT-enabled predictive maintenance reduces healthcare equipment downtime by 20%-30%, saving millions in lost revenue annually.
Source: Deloitte
Thought Leadership: The Road Ahead As healthcare facilities transition to smarter and more sustainable operations, they set a precedent for the future of the industry. Success will depend on innovation, collaboration, and a commitment to long-term sustainability.
The transition to smart integration and electrification in Australian healthcare facilities is an opportunity to redefine the sector’s sustainability and operational standards. Success lies in:
Long-Term Vision: Planning for capital investments with a focus on lifecycle cost optimization and infrastructure resilience.
Collaborative Ecosystems: Engaging government, private sector, and healthcare providers to share knowledge and resources.
Technological Adaptation: Proactively adopting advancements in electrification and smart systems to maintain a competitive edge.
By prioritizing these elements, Australia’s healthcare sector can lead in delivering sustainable, efficient, and patient-centric facilities for generations to come.
With healthcare facilities saving millions annually in energy costs and achieving significant reductions in carbon footprints, the value propositions for smart integration and electrification are compelling. By embracing these advancements, Australia’s healthcare sector is poised to lead in creating sustainable, efficient, and patient-centric facilities.










Comments